EU Accessibility Act in the Nordics: Consistent, Contextual, and Culturally Anchored
In our previous articles, we outlined how countries like France, Poland, Germany, and the Netherlands have implemented the Accessibility Directive, so it’s time to have a closed view to European Accessibility Act in the Nordics region. Sweden, Denmark, Finland, and Norway stand out for its long-standing digital accessibility culture. These countries are not starting from scratch: accessibility is already a legal and social expectation.
In this article, we examine how the European Accessibility Act applies across the Nordics and what companies need to prepare for, whether they operate locally or cross-border.
How the European Accessibility Act Affects Nordic Businesses?
The Nordic approach to the EAA is marked by integration rather than reinvention. Instead of building entirely new frameworks, each country has chosen to embed the EAA into existing national legislation. This reflects the region’s long tradition of treating accessibility as both a legal right and a cultural norm.
- Sweden has incorporated the EAA into Lag (2023:254), broadening its existing accessibility framework to cover sectors such as banking, e-commerce, transport, and telecom. Oversight is shared between the Swedish Consumer Agency (Konsumentverket) and the Agency for Digital Government (DIGG).
- Denmark enforces accessibility through Act no. 801 of 07/06/2022, with a strong emphasis on consumer protection. The Danish Business Authority (Erhvervsstyrelsen) is the lead body, taking a guidance-led approach while retaining the power to issue fines and corrective measures.
- Finland aligns the EAA with Government Decrees 179/2023 and 180/2023, building on the accessibility requirements already established under the Act on the Provision of Digital Services. Compliance is supervised by the Finnish Transport and Communications Agency (Traficom).
- Norway, while not an EU member, implements equivalent rules via the Anti-Discrimination and Accessibility Act and related ICT regulations. Enforcement is handled by the Agency for Public Management and eGovernment (Digdir), ensuring alignment with the EEA Agreement.
For businesses, this creates continuity with national traditions but also complexity: obligations are consistent in principle, yet enforcement models and regulatory expectations differ across the region. Multinationals must be prepared to navigate these nuances while ensuring compliance with a baseline set of EAA requirements.
What the European Accessibility Act in the Nordics Requires?
The baseline obligations are the same across all Nordic countries, as they derive from the EU Directive:
- Digital content must comply with WCAG 2.1 AA (websites, apps, PDFs)
- Products and services must be compatible with assistive technologies
- Accessibility statements, documentation, and feedback mechanisms are mandatory
- Labels, instructions, and user interfaces must be legible, perceivable, and understandable
- Identification, security, and payment functions must meet POUR principles
Banking and e-commerce services carry extra requirements:
- Identification methods, e-signatures, and payment services must be perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust
- Financial information must be written at B2 language level or lower, ensuring clarity
- E-commerce operators must provide information about the accessibility of products and services where available
This mirrors the approach in the Netherlands and highlights how financial services are under special scrutiny across the EU, including the Nordics.
Exemptions and Exceptions for European Accessibility Act in the Nordics
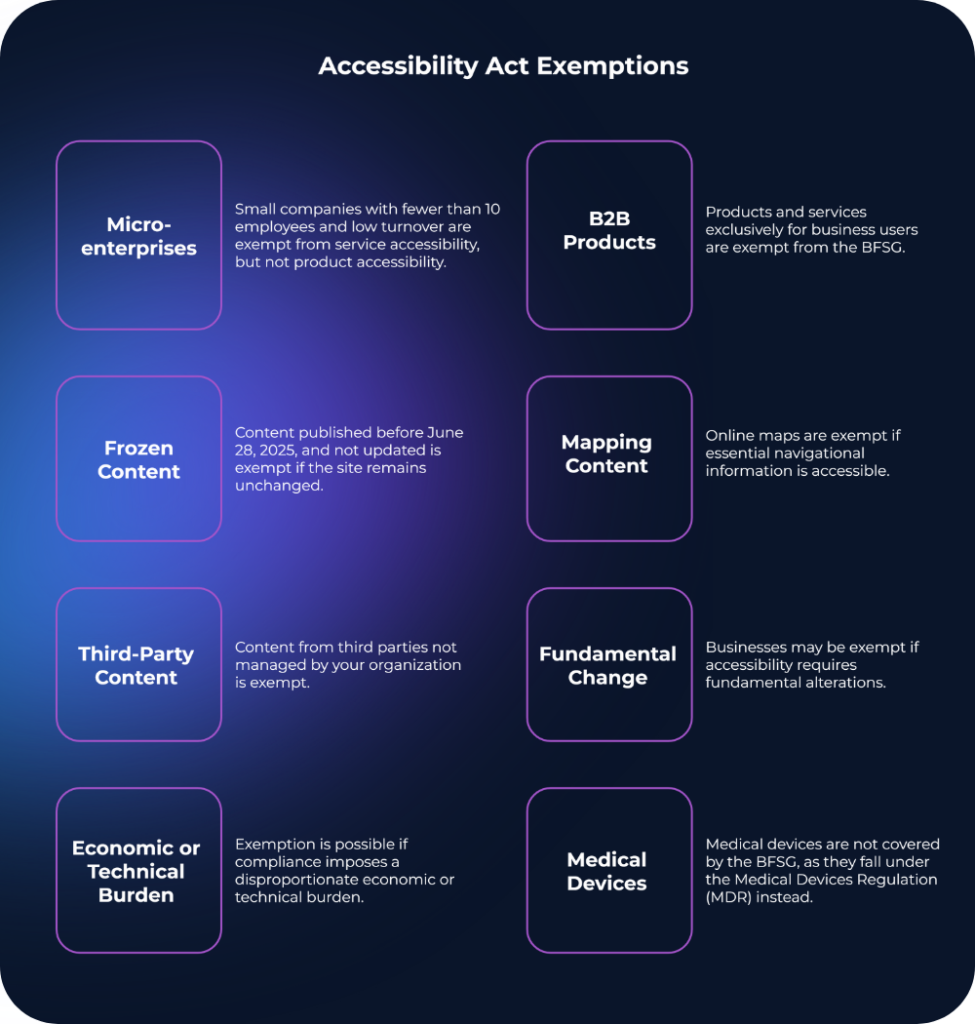
The Nordic countries follow the general EAA exemptions:
- Microenterprises: Fewer than 10 employees and turnover/balance sheet below €2M are exempt. Regulators in Sweden, Denmark, and Finland nevertheless encourage voluntary compliance to remain competitive in the digital single market.
- Disproportionate burden: Businesses may be exempt if compliance would create costs disproportionate to the accessibility benefit, based on Annex VI of the Directive. Lack of time or knowledge is not a valid reason.
- Fundamental alteration: When accessibility requirements would alter the service so substantially that it becomes a different service.
- B2B services: The EAA applies only to business-to-consumer services, not pure B2B contexts.
Timeline and Transition Rules
The enforcement date is consistent across the EU and the EEA:
- 28 June 2025: All new services and modified contracts must comply with the EAA
- Existing contracts signed before this date may run until expiry, but no longer than five years, meaning by 28 June 2030 all must comply
- Physical products used in service delivery (e.g., payment terminals, e-ID devices) have the same five-year transition period. Products placed on the market before June 2030 may be used temporarily, but must be upgraded or replaced to meet the new requirements
What Penalties for Non-Compliance in the Nordic Region?
The penalty framework varies slightly across Nordic countries, but follows similar patterns:
- Administrative fines are the main tool, with amounts depending on turnover and severity
- Regulators may impose recurring penalties until compliance is achieved
- In serious cases, providers may face suspension of services or public disclosure of violations
Sweden’s model is considered stricter, with higher fines and stronger inspection powers, while Denmark and Finland lean on consumer law enforcement traditions.
Key Differences at a Glance for Nordic Countries
To make the national differences clearer, the table below outlines how each Nordic country has embedded the EAA into its legal framework, who supervises compliance, and what businesses should be aware of in terms of scope and enforcement.
| Country | Main Law / Framework | Supervisory Authority | Special Features | Penalties & Enforcement |
| Sweden | Lag (2023:254) | Swedish Consumer Agency (Konsumentverket) and Agency for Digital Government (DIGG) | Broad scope, covering banking, e-commerce, transport, and telecom; one of the earliest comprehensive accessibility laws in Europe. | Fines, corrective orders, and strong inspection powers; considered among the strictest in the EU. Fines range up to EUR 200 000. |
| Denmark | Act no. 801 of 07/06/2022 | Danish Business Authority (Erhvervsstyrelsen) | Strong consumer protection focus; guidance-led enforcement with emphasis on business accountability. | Administrative fines, warnings, and recurring penalties until compliance is achieved. Fines range up to EUR 10 000 for initial non-compliance. |
| Finland | Government Decrees 179/2023 & 180/2023 | Finnish Transport and Communications Agency (Traficom) | Builds on existing Digital Services Act (2019), where WCAG 2.1 AA was already mandatory for public bodies. | Fines and corrective measures, applied proportionately to scale and impact. Fines range up to EUR 150 000. |
| Norway (EEA country) | Anti-Discrimination and Accessibility Act + ICT regulations | Agency for Public Management and eGovernment (Digdir) | Applies to both public and private services despite Norway being outside the EU; aligns with EEA obligations. | Administrative penalties and corrective measures, supported by Norway’s strong ICT audit tradition. |
Summary
The Nordics are well-positioned to implement the EAA thanks to their strong pre-existing accessibility laws. For businesses, this means compliance is not just about meeting EU standards but aligning with national frameworks that often go further.
From Sweden’s early adoption of a broad accessibility act, to Norway’s strict ICT obligations, the Nordic region sets high expectations. Companies operating here must take accessibility seriously, integrate it into product and service design from the outset, and prepare for close scrutiny by multiple regulators.
European Accessibility Act in the Nordics region is treated as integral to society, law, and commerce, rather than as a formal obligation alone.