EU Accessibility Act in Poland: Details Business Should Know
The European Accessibility Act (EAA) is reshaping how businesses in Europe design and deliver digital services. In our previous article, we shared the main pillars and risks of being incompliant with the European Accessibility Act. Let’s go beyond the common European directive and dive deeper with state-centred approaches.
In this article, we share all you need to know to operate in an EAA-compliant way in Poland, despite being a local or global company.
How European Accessibility Act Affects Poland Business?
Poland’s national implementation of the European Accessibility Act (Directive 2019/882) goes well beyond the EU baseline — introducing stricter obligations, more detailed formatting rules, and a robust enforcement framework. Businesses operating in Poland must prepare not only for compliance with the directive, but also with a more prescriptive and locally integrated legal environment.
What EAA or PAD (Polski Akt Dostępności) in Poland Requires?
- Digital content must comply with WCAG 2.1 AA (e.g., readable PDFs, accessible websites)
- Products and services must work with assistive technologies
- Clear labelling and instructions with adequate font size, spacing, and contrast
- Online documentation must be publicly available and accessible
- Businesses must show evidence of accessibility efforts (technical documentation, testing, declarations)
Exemption for Microenterprises
While the EU directive gives Member States the option to exempt microenterprises, Poland applies this exemption across the board.
This means:
- Businesses with fewer than 10 employees;
- Either less than €2 million in turnover or balance sheet total.
This narrows the scope considerably for very small businesses, while placing greater responsibility on SMEs and large enterprises.
Controlled Exemptions for Mapping and Navigation
While the EU directive allows certain exemptions for mapping and navigation systems, the Polish Act narrows these significantly.
Interactive maps and geoportals are only exempt if:
- The data present is already available in a digitally accessible format, and
- The service complies with Poland’s separate Digital Accessibility Act (2019), which governs public sector websites and apps.
This layered approach ensures that accessibility gaps aren’t created through overly broad expectations. The relevant provisions are found in Article 4(2)(a).
Other Exemptions
The Act also outlines specific cases where accessibility obligations do not apply. These include:
- Third-party content not funded, developed, or controlled by the economic operator;
- Public transport services and local administrative services at the municipal, metropolitan, county, and county-municipal levels, unless otherwise required under other Polish or EU regulations.
These limited exemptions recognize practical constraints while maintaining the overall intent of the law — ensuring accessibility is the rule, not the exception.
Disclosure Rules for Physical and Digital Accessibility
The Polish Accessibility Act does more than require accessibility — it defines how accessibility must be implemented. However, it stops short of listing exact technical specifications. Instead, it refers broadly to “essential accessibility requirements defined in EU law and harmonized standards.”
To navigate this ambiguity, we recommend aligning with the two primary standards recognized across the EU for demonstrating compliance:
- EN 301 549 – the harmonized European standard for ICT accessibility
- WCAG 2.1 – the global benchmark for digital content accessibility (incorporated within EN 301 549)
These standards outline specific, testable criteria across both physical and digital domains:
For Physical Products
- Labels and instructions must meet defined criteria for font size, color contrast, and text spacing, ensuring legibility for users with visual impairments.
- Information must be perceivable through multiple sensory channels, supporting accessibility for people with visual, auditory, or cognitive disabilities.
For Digital Documentation
- Documentation must be made available online in an accessible format, compliant with WCAG and EN 301 549.
- The web address (URL) for this digital content must be clearly printed on the physical product or its packaging.
- All content must be compatible with assistive technologies, including:
- Screen readers (e.g., NVDA, JAWS)
- Braille displays
- Alternative and Augmentative Communication (AAC) systems
By proactively meeting these harmonized standards, organizations can demonstrate good-faith compliance with the Polish Accessibility Act and reduce their exposure to regulatory risk.
Tightly Defined Legal Terms
Where the EU directive leaves room for interpretation, the Polish legislation introduces precise legal definitions for key accessibility terms. These include:
- User interface accessibility – ensuring digital tools are operable, understandable, and robust for all users
- Real-time communication – defined to include voice, video, and text channels that enable seamless, synchronous interaction
- Alternative and Augmentative Communication (AAC) – explicitly referenced, supporting individuals with speech or language impairments
- Interoperability with assistive technologies – a requirement for ensuring systems work across platforms and devices, not just within proprietary environments
This increased specificity supports legal certainty and simplifies implementation for both product developers and compliance teams.
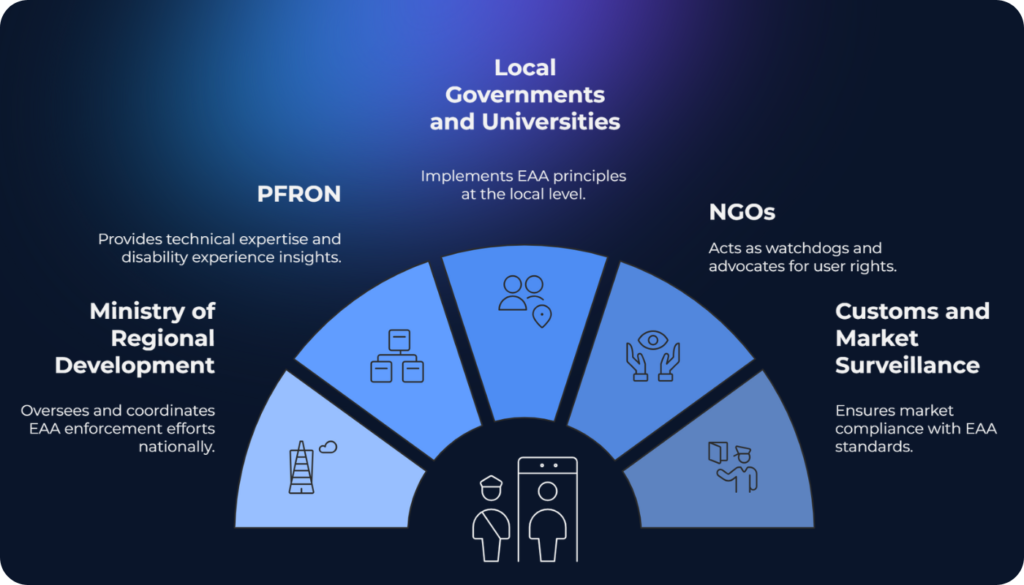
Multi-Institutional Enforcement Model
Enforcement in Poland will not rely on a single regulator. Instead, it is distributed across multiple institutions to ensure cross-sector compliance:
- The Ministry of Regional Development serves as the coordinating body
- PFRON (State Fund for Rehabilitation of Disabled Persons) supports monitoring and expertise
- Local governments and universities are involved in outreach and technical assistance
- NGOs focused on accessibility provide oversight and advocacy
- Customs and market surveillance authorities handle inspections and enforcement in import/export and retail contexts
Monitoring begins in June 2026, following the mandatory compliance date of 28 June 2025.
Integration Across Over 10 Domestic Laws
To create a consistent and enforceable framework, Poland has embedded the a wide range of existing legislation, including:
- Public Procurement Law – ensuring accessibility is considered in purchasing decisions
- Telecommunications Law – covering accessibility in communication networks and devices
- Payment Services Act – affecting the usability of payment terminals and online services
- Transport and emergency systems legislation – ensuring access to public transport, alerts, and emergency services
- Act on accessibility for persons with special needs (2019) building on existing standards to harmonise legal obligations across sectors
This cross-law integration makes accessibility a mandatory design principle — not a compliance afterthought. It introduces measurable expectations for both product and service delivery, reinforces risk exposure in regulated environments and aligns national policy with EU enforcement strategy. This integration supports systemic change and positions accessibility as a core requirement, not a side consideration.
Summary
Poland’s approach to accessibility is comprehensive and future-facing. For companies operating in Poland, or exporting to it, compliance with the Polish Accessibility Act requires more than checking boxes. It demands deliberate design choices, legal awareness, and operational readiness. Starting early will reduce risk and help businesses deliver inclusive experiences that meet both regulatory and customer expectations.

